Implementing smart contracts involves several steps, and the specific details may vary depending on the blockchain platform you are using. Remember that implementing smart contracts requires a good understanding of blockchain technology, programming, and security best practices. Regularly update your knowledge as the field evolves quite fast, and stay informed about any updates or changes to the blockchain platform you are using. Moreover, consider seeking advice from experienced developers and engaging with the blockchain community for support and collaboration.

Here are eight (8) general steps that can serve as a guideline:
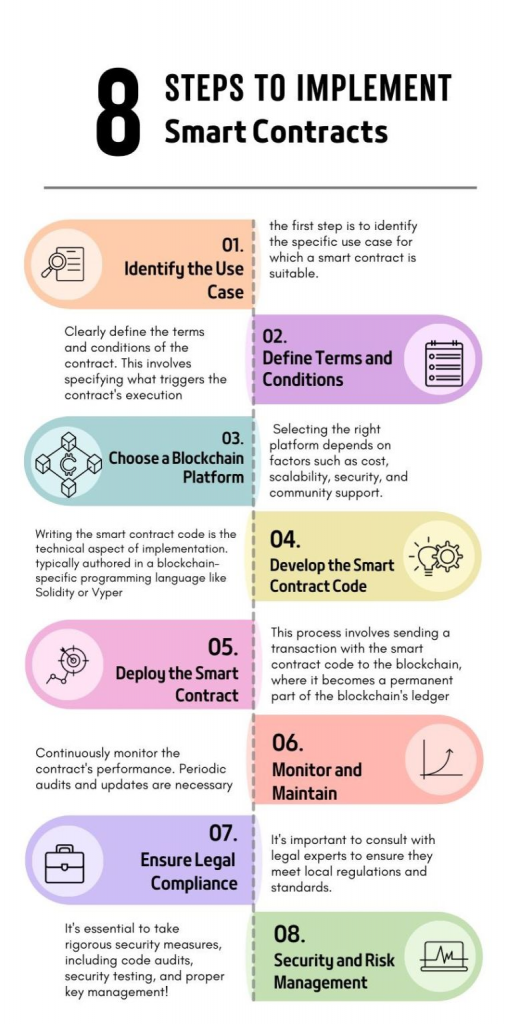
- Define the Purpose and Requirements
Clearly define the purpose of your smart contract and outline the requirements it needs to meet. Understand the problem you are solving and identify the key functionalities the smart contract should have. - Choose a Blockchain Platform
Select a blockchain platform that supports smart contracts. Ethereum is one of the most popular choices, but others like Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and Polkadot also support smart contracts. The choice may depend on factors such as transaction speed, cost, and the specific features offered by the platform. - Set Up Development Environment
Install the necessary development tools and set up your development environment. For Ethereum, this might involve installing the Solidity compiler, a development framework like Truffle, and an Ethereum client like Ganache for testing. - Write Smart Contract Code
Use a programming language supported by the chosen blockchain platform to write the smart contract code. Solidity is commonly used for Ethereum. Ensure that your code adheres to best practices, is secure, and meets the specified requirements. - Compile and Test
Compile the smart contract code into bytecode. Test the smart contract on a local blockchain or a testnet to identify and fix any issues. Testing is crucial to ensure the contract behaves as expected and is secure. - Deploy to the Blockchain
Once testing is successful, deploy the smart contract to the mainnet or the desired blockchain. Deploying to the mainnet involves real cryptocurrency transactions, so make sure to double-check your code and test thoroughly before deploying. - Verify and Audit
After deployment, verify the smart contract on the blockchain to provide transparency and ensure that others can confirm its legitimacy. Consider conducting a security audit by professionals to identify and address any vulnerabilities in the code. - Interact with the Smart Contract
Develop and deploy a user interface or backend system that interacts with the smart contract. Users should be able to interact with the smart contract using your application, invoking its functions and viewing relevant data.
xxx



