Kingdom of Saudi Arabia | المملكة العربية السعودية (Arabic)
Al-Mamlakah al-ʿArabīyah as-Suʿūdīyah
| Capital and Largest City | Riyadh 24°39′N 46°46′E 24°39′N 46°46′E |
|---|
Saudi Arabia is a vast country with diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a mix of modern and traditional elements. Traveling in Saudi Arabia can be a unique and rewarding experience.
Here are some things to know about traveling in Saudi Arabia:
Visa Requirements: Most travelers to Saudi Arabia will need a visa to enter the country. The type of visa and requirements can vary depending on your nationality and the purpose of your visit. It’s essential to check the specific visa requirements and apply in advance.
Entry requirements
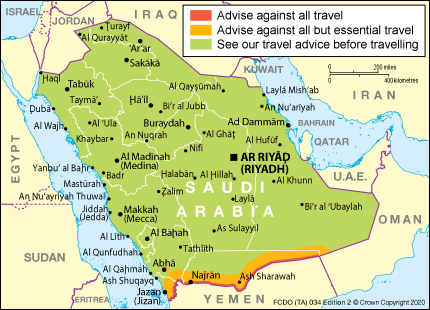
This page has information on travelling to Saudi Arabia.
This page reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British Citizen passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Saudi Arabia set and enforce entry rules. If you’re unsure how Saudi Arabia’s entry requirements apply to you, contact its UK embassy, high commission, or consulate.
Exit and re-entry permits
British residents in Saudi Arabia will need a valid exit or re-entry permit from the Saudi Ministry of Interior to leave and re-enter the country.
Local laws and customs
Saudi Arabia is a Muslim country in which Islamic law is strictly enforced. You should respect local traditions, customs, laws, and religions at all times and be aware of your actions to ensure that they do not offend, especially during the holy month of Ramadan or if you intend to visit religious areas.
You can read more about living in Saudi Arabia here.
Culture: Saudi Arabia is a conservative country with strict Islamic laws and customs. Visitors should be respectful of local traditions and adhere to the country’s dress code, which includes modest clothing, particularly for women.
Language: Arabic is the official language, but English is widely spoken, especially in urban areas and among the younger population. Learning a few basic Arabic phrases can be helpful and appreciated.
Transportation: Saudi Arabia has a modern transportation infrastructure. Major cities like Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam have well-developed road networks and public transportation systems. Domestic flights are also common for traveling between cities due to the country’s vast size.
Tourist Attractions: Saudi Arabia offers a range of tourist attractions, including historical sites like Diriyah, Al-Ula with its UNESCO World Heritage-listed rock formations, the Red Sea coast for diving and snorkeling, and the Empty Quarter desert for adventurous travelers.
Religious Tourism: Saudi Arabia is home to two of the holiest cities in Islam, Mecca, and Medina. While non-Muslims are not allowed to enter these cities, the country’s religious significance is essential to understand when visiting other areas.
Accommodation: Saudi Arabia has a range of accommodation options, from luxury hotels to budget-friendly choices. Major cities have a variety of international hotel chains.
Food: Saudi Arabian cuisine features dishes like Kabsa (spiced rice with meat), Mandi (similar to Kabsa), Shawarma, and various types of bread, including flatbreads like Khubz. Traditional Arabic coffee (Gahwa) and dates are often offered as a sign of hospitality.
Safety: Saudi Arabia is generally considered safe for tourists, with low crime rates. However, it’s essential to stay informed about local regulations and follow the country’s laws and customs.
Entertainment: In recent years, Saudi Arabia has been opening up to more entertainment options, including concerts, cinema, and cultural events, as part of its efforts to promote tourism and diversify its economy.
Shopping: Saudi Arabia has modern shopping malls and traditional souks (markets) where you can purchase traditional clothing, handicrafts, spices, and more.
Before traveling to Saudi Arabia, it’s advisable to check the latest travel advisories, visa requirements, and any specific regulations that may apply to your visit. Saudi Arabia is continually evolving as a tourist destination, offering a mix of ancient history and modern development for travelers to explore.
Events and Festivals: The country hosts various cultural and religious festivals throughout the year. The most significant event is the Hajj, which attracts millions of Muslim pilgrims from around the world.
xxx
| Establishment | |
|---|---|
| • Emirate of Diriyah | 1727 |
| • Emirate of Nejd | 1824 |
| • Emirate of Riyadh | 13 January 1902 |
| • Unification | 23 September 1932 |
| • Admitted to the United Nations | 24 October 1945 |
| • Current Constitution | 31 January 1992 |
Local Laws of Saudi Arabia
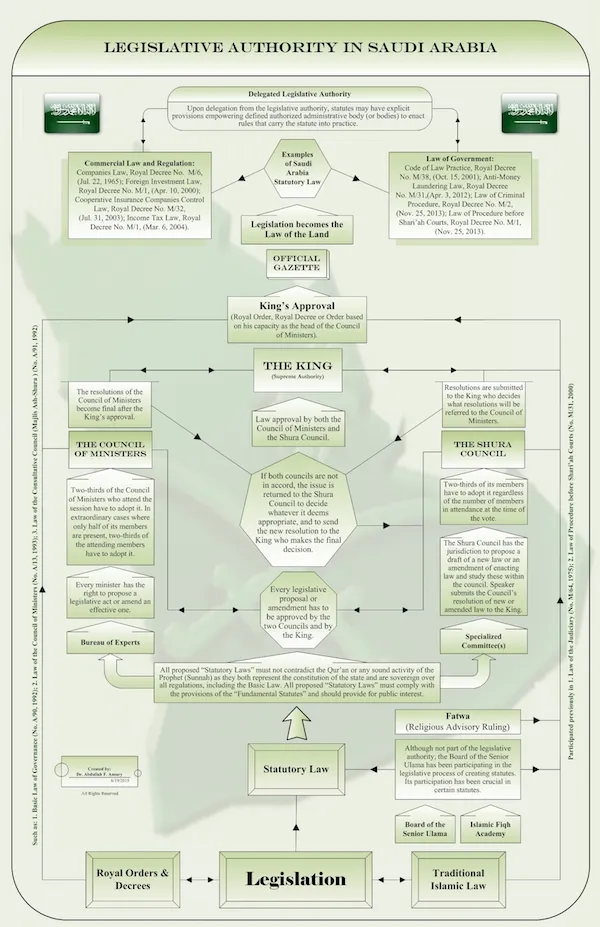
Saudi Arabia follows a legal system based on Islamic law, known as Sharia law. Sharia law serves as the foundation for the country’s legal framework, and it plays a central role in various aspects of life in Saudi Arabia.
Here are key aspects of the local law in Saudi Arabia:
- Islamic Law (Sharia): Sharia law governs many aspects of personal and public life in Saudi Arabia, including matters related to family law, criminal law, and moral conduct. Islamic jurisprudence guides legal decisions and interpretations.
- Religious Police: The country has a religious police force known as the Committee for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice (known as the Mutaween). They are responsible for enforcing Islamic moral and ethical standards in public places.
- Family Law: Family matters, such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance, are governed by Islamic family law. Men and women have distinct rights and responsibilities in these matters, and the legal age for marriage is 18 for males and 16 for females.
- Dress Code: There is a strict dress code in Saudi Arabia, with a requirement for modest clothing, particularly for women. Women are required to wear an abaya (a long black cloak) in public.
- Criminal Justice: The Saudi legal system employs both Islamic law and a set of regulations and statutes. Punishments for certain offenses can be severe and may include corporal punishment, fines, imprisonment, or even the death penalty.
- Alcohol and Pork: The consumption and possession of alcohol and pork products are strictly prohibited in Saudi Arabia.
- Public Conduct: Public behavior and conduct are expected to adhere to Islamic principles. Public displays of affection, as well as other behaviors deemed contrary to Islamic values, are not allowed.
- Freedom of Religion: Saudi Arabia officially practices and promotes Sunni Islam. The public practice of religions other than Islam is restricted, and non-Muslim places of worship are not permitted.
- Business and Contracts: Commercial and business transactions are governed by a combination of Islamic law and modern commercial regulations. Contracts and business dealings often include Sharia-compliant financial practices.
- Entertainment: In recent years, Saudi Arabia has been working to expand its entertainment and cultural offerings. Cinemas, concerts, and other forms of entertainment are now more accessible to the public as part of efforts to diversify the country’s economy and promote tourism.
It is important for visitors and expatriates in Saudi Arabia to be aware of and respect the country’s legal and cultural norms. Laws and regulations can vary, so it is advisable to consult with local authorities or legal experts when in doubt about specific matters.
Additionally, Saudi Arabia has been undergoing reforms in recent years, with some changes aimed at modernizing aspects of the legal and cultural landscape.

xxx
History of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, as a unified nation-state, began to take shape in the early 20th century. The establishment of the modern Kingdom of Saudi Arabia can be attributed to a series of events, including the following key milestones:
- 18th Century: The Arabian Peninsula was historically divided into various tribal regions and emirates. The central and western regions of the peninsula were inhabited by tribes that adhered to the strict interpretation of Sunni Islam known as Wahhabism. This laid the foundation for the religious and cultural identity of the region.
- 1744: Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, an Islamic scholar, formed an alliance with Muhammad ibn Saud, a tribal leader. This alliance laid the groundwork for the First Saudi State, with Riyadh as its capital. The union aimed to propagate the teachings of Wahhabism and establish a strict Islamic state.
- 19th Century: The First Saudi State was short-lived and faced conflicts with the Ottoman Empire. It collapsed in the early 19th century.
- 1902: Abdulaziz Ibn Saud (also known as Ibn Saud) recaptured Riyadh, marking the beginning of the expansion of the Second Saudi State. Over several decades, he and his descendants gradually unified and expanded their control over various regions of the Arabian Peninsula.
- 1932: Abdulaziz Ibn Saud officially declared the establishment of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia on September 23, 1932, with himself as the monarch. This marked the unification of the major tribal regions into a single nation-state.
- 20th Century: Saudi Arabia continued to evolve politically and economically during the 20th century. The discovery of vast oil reserves in the country in the late 1930s transformed its economy and played a significant role in its global influence.
- 21st Century: In recent years, Saudi Arabia has undergone various socio-economic and cultural reforms under the leadership of successive kings, with efforts to diversify the economy, expand women’s rights, and promote tourism.
So, while the region that is now Saudi Arabia has a deep historical and cultural heritage dating back centuries, the modern nation-state of Saudi Arabia, as it exists today, was officially founded in 1932 by Abdulaziz Ibn Saud.
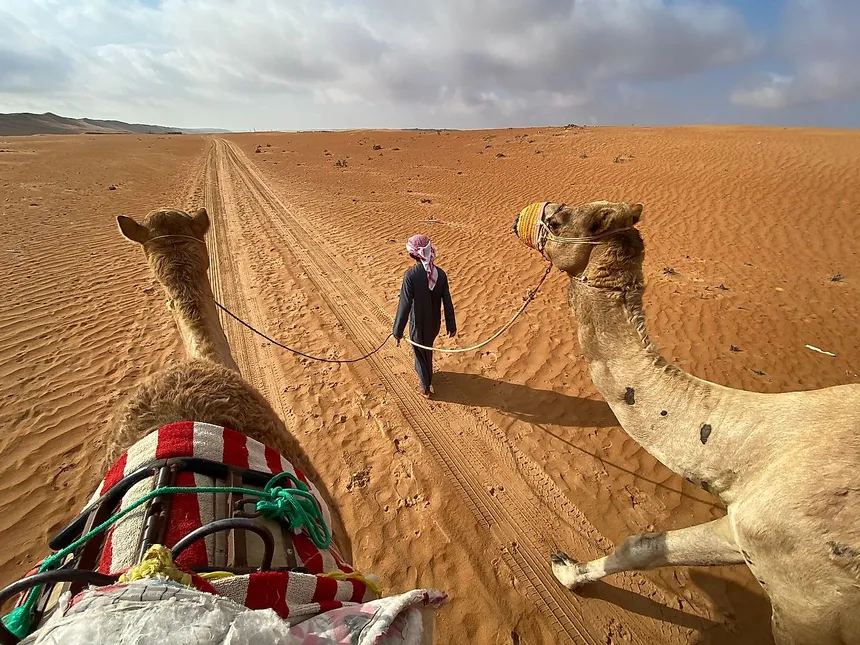

Fun Fact about Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is home to the largest continuous sand desert in the world, known as the Rub’ al Khali or the Empty Quarter. This massive desert covers a significant portion of the Arabian Peninsula, including parts of Saudi Arabia, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The Rub’ al Khali spans approximately 650,000 square kilometers (about 250,000 square miles), making it larger than many countries.
This desert is not only vast but also incredibly arid, with some of the highest sand dunes in the world, reaching heights of over 300 meters (almost 1,000 feet). It’s a harsh and challenging environment, but it’s also a place of natural beauty and unique landscapes, attracting adventurous travelers and desert enthusiasts from around the world.
XXX
عربي
الانفجار النوعي في علم الأوعية هو حالة طبية تتميز بتمدد محلي غير طبيعي أو انتفاخ في الأوعية الدموية. يمكن أن تحدث الانفجارات في الشرايين أو الأوردة، ولكنها ترتبط عادة بالشرايين بشكل أكبر، ولا سيما الشرايين التي تنقل الدم المؤكسج بعيدًا عن القلب، مثل الأبهراء (الشريان الرئيسي للجسم) أو الشرايين الدماغية (الشرايين في الدماغ). يمكن أيضًا حدوث الانفجارات في الشرايين التابعة لأعضاء أخرى في الجسم.
هناك أنواع مختلفة من الانفجارات، بما في ذلك:
- الانفجارات الأبهرائية: تحدث هذه في الأبهراء، وهي أكبر شريان في الجسم. يمكن أن تتواجد الانفجارات الأبهرائية في الصدر (الانفجارات الأبهرائية في الصدر) أو في البطن (الانفجارات الأبهرائية في البطن). إنها قد تشكل تهديدًا للحياة إذا انفجرت.
- الانفجارات الدماغية: تحدث هذه في الشرايين الموجودة في الدماغ. يمكن أن يؤدي انفجار الانفجار الدماغي إلى نوع من السكتة الدماغية تسمى النزيف تحت العنكبوتية.
- الانفجارات الأطراف: تحدث هذه في الشرايين خارج القلب والدماغ، مثل الساقين أو الذراعين.
يمكن أن تسبب الانفجارات بواسطة عوامل متنوعة، بما في ذلك:
- ضعف في جدار الأوعية الدموية.
- ارتفاع ضغط الدم (ارتفاع ضغط الدم).
- تصلب الشرايين (تصلب الشرايين).
- العدوى أو التهاب جدار الأوعية الدموية.
- إصابة أو ضرر في الأوعية الدموية.
- عوامل وراثية (قد يكون بعض الأفراد أكثر تمايلًا لتطوير الانفجارات).
يمكن أن تختلف الانفجارات من حيث الحجم والشكل والموقع. قد لا تسبب الانفجارات الصغيرة أعراضًا ملحوظة ويمكن أن تمر دون اكتشاف لسنوات. ومع ذلك، الانفجارات الأكبر حجمًا معرضة لمخاطر أكبر للانفجار، مما يمكن أن يؤدي إلى نزيف شديد وعواقب قد تهدد الحياة. يمكن أن تتضمن أعراض انفجار الانفجار فجائية وحادة، فقدان الوعي، وانخفاضات عصبية أخرى.
تعتمد علاج الانفجارات على حجمها وموقعها والحالة الصحية العامة للفرد. قد يتم مراقبة الانفجارات الصغيرة والمستقرة عن كثب دون تدخل فوري. قد تتطلب الانفجارات الأكبر حجمًا أو ذات المخاطر العالية إصلاحًا جراحيًا أو إجراءات وعائية لمنع الانفجار.
الكشف المبكر والإدارة هما أمران حاسمان للوقاية من المضاعفات المرتبطة بالانفجارات، خاصةً تلك التي تحتمل خطر الانفجار. قد يُنصح بإجراء فحوصات منتظمة للأفراد الذين يعانون من عوامل الخطر للانفجارات، مثل التاريخ العائلي أو بعض الحالات الطبية، واتباع توصيات مقدم الرعاية الصحية لاتخاذ التدابير الوقائية.

xxx




One thought on “Saudi Arabia المملكة العربية السعودية ✈️ Travel”